Accountants also often use this ratio since accounting deals closely with reporting assets and liabilities on financial statements. Companies with a healthy current ratio are often viewed as being more creditworthy and better able to meet their short-term obligations. Low values for the current ratio (values less than 1) indicate that a firm may have difficulty meeting current obligations.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
- Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
- Company A has more accounts payable while Company B has a greater amount of short-term notes payable.
- Creditors are more willing to extend credit to those who can show that they have the resources to pay obligations.
- Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
- Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
A large retailer like Walmart may negotiate favorable terms with suppliers that allow it to keep inventory for longer periods and have generous payment terms or liabilities. This article and related content is the property of The Sage Group plc or its contractors or its licensors (“Sage”). Please do not copy, reproduce, modify, distribute or disburse without express consent from Sage.This article and related content is provided as a general guidance for informational purposes only. This article and related content is not a substitute for the guidance of a lawyer (and especially for questions related to GDPR), tax, or compliance professional. When in doubt, please consult your lawyer tax, or compliance professional for counsel.
How Is the Current Ratio Calculated?
We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other what is the difference between a sales return and a sales allowance factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Editorial Independence

Potential creditors use this ratio in determining whether or not to make short-term loans. The current ratio can also give a sense of the efficiency of a company’s operating cycle or its ability to turn its product into cash. There’s another common ratio used to look at a company’s liquidity — the quick ratio. Unlike the current ratio, which considers all current assets and liabilities, the quick ratio only looks at the most liquid assets (although it does include accounts receivable) versus the current liabilities. Other similar liquidity ratios can be used to supplement a current ratio analysis. In each case, the differences in these measures can help an investor understand the current status of the company’s assets and liabilities from different angles, as well as how those accounts are changing over time.
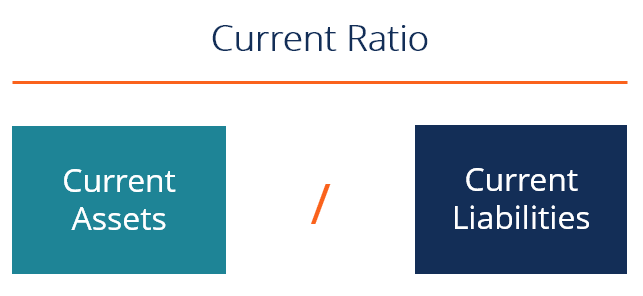
Current Ratio Formula
Apple technically did not have enough current assets on hand to pay all of its short-term bills. Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements. Creditors use it to gauge a company’s ability to repay loans, while investors gain insights into its short-term financial stability.
So a current ratio of 4 would mean that the company has 4 times more current assets than current liabilities. It is important to note that a similar ratio, the quick ratio, also compares a company’s liquid assets to current liabilities. However, the quick ratio excludes prepaid expenses and inventory from the assets category because these can’t be liquified as easily as cash or stocks. The current ratio is balance-sheet financial performance measure of company liquidity. The current ratio indicates a company’s ability to meet short-term debt obligations. The current ratio measures whether or not a firm has enough resources to pay its debts over the next 12 months.
The cash asset ratio (or cash ratio) is also similar to the current ratio, but it compares only a company’s marketable securities and cash to its current liabilities. This ratio compares a company’s current assets to its current liabilities, testing whether it sustainably balances assets, financing, and liabilities. Typically, the current ratio is used as a general metric of financial health since it shows a company’s ability to pay off short-term debts. The current ratio is a metric used by accountants and finance professionals to understand a company’s financial health at any given moment. This ratio works by comparing a company’s current assets (assets that are easily converted to cash) to current liabilities (money owed to lenders and clients). To calculate the ratio, analysts compare a company’s current assets to its current liabilities.
The best long-term investments manage their cash effectively, meaning they keep the right amount of cash on hand for the needs of the business. The current ratio is part of what you need to understand when investing in individual stocks, but those investing in mutual funds or exchange-trade funds needn’t worry about it. For instance, the liquidity positions of companies X and Y are shown below. For example, supplier agreements can make a difference to the number of liabilities and assets.
Calculating the current ratio at just one point in time could indicate that the company can’t cover all of its current debts, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that it won’t be able to when the payments are due. The cash ratio is ideal for assessing immediate liquidity without assuming future collections, but it may be too conservative for businesses that collect payments reliably, like SaaS or professional services. The quick ratio focuses on assets that can be converted to cash quickly, such as cash reserves and receivables, and shows your company’s financial flexibility and resilience. Current liabilities are obligations that are due to be paid within one year.
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
Leave a Reply